HTML And Front-end Architecture

The C&C #LadyDevs

Amy Norris
Director

Alex Herron
Co-Director

Julie Batson
Curriculum Director

Gabi Dombrowski
Mentor Director

Kim Watt
Marketing Director

Vanessa Shultz
Co-Presentation Director

Alicia Villegas
Co-Presentation Director

Tracy Hockenhull
Technical Materials Director
Our Host this Evening
Drinks Served

Laura Kozak
Join us on...

#codingandcocktails
- #kc-jobs
- #generalchat
- #events
- #techtalks
- #announcements
- #interesting-times-initiative
Our mentors

are super heroes!
Before We Get Started...
This stuff is a challenge!
Don’t be discouraged if you don’t finish each worksheet section before the next presentation section begins.
We cover a lot of difficult material that will take time to understand. We are here (and on Slack after the session) to help!
Tonight's Agenda:
HTML & Front-end Architecture
- What is Web Development & Intro to HTML
- HTML Content Tags
- HTML Attributes & the DOM
- Accessibility (A11y)
- Intro to Front-End Architecture
What is Web Development?
- Tasks involved in creating, building, and maintaining websites and applications that run online on a browser
What is a Website?
- Special files that browsers can read and display as the websites we use daily
Website files include:
- Code files: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Extra files: images & videos
Code Files Include:
- HTML - content you see
- CSS - styles for the site
- JavaScript - defines behavior of the website
HTML | Content
- Defines the structure of the content (navigation, header, footer, lists)
- Organizes the content, but it doesn't handle the layout
- Looks plain on its own
- Our focus for today
CSS | Styling
- Decorates HTML content by adding visual appeal
- Handles layout of content
- Join us for our next session to dive into CSS!

JavaScript | Behavior
- Muscles that power a website
- Handles interactions, such as button clicks, and fetches dynamic content to keep information up to date
- Join us later this year when we cover JavaScript
Imagine a house:

How do they fit together?
- HTML is the structure (walls, floors, and foundation)
- CSS is the paint, decorations, and design
- JavaScript is the electricity and plumbing that makes things interactive
HTML Basics

What is HTML?
Hyper
Text
Markup
Language
HTML continued...
- A language with specific rules that tells the browser how to display the content
- Defines the meaning and structure of the content, not its appearance
- The most essential component of webpages
HTML continued...
- Type (header, body) versus style (font, color, background)
- HTML files have a .html extension
- Edited with plain text editor / IDE (Integrated Development Environment)
- Windows Notepad or Mac TextEditor
Where in the World Would You See HTML?

Where in the World Would You See HTML?
- index.html:
main entry to a website (like your website homepage) - Every website has at least one index.html file
- We'll see an example of this in our project tonight
HTML Syntax

Tags
- Tell browser how to display content inside
- Book-ends (most cases, you have to have a pair: opening tag and closing tag)
Open/Close Tags
The opening tag has the tag name in angle brackets (< >)
The closing tag has a forward slash ( / ) before the tag name (< />)
Open/Closed Tags
Example from MDN:

More About Open and Close Tags
More HTML elements can be inside tags
Example from MDN:
<div>
<p>
My cat is very <em>very</em> grumpy.
</p>
</div>
My cat is very grumpy.

Self-closing Tags
<img src="../images/ryan-gosling.gif" height="300vh" />

Required HTML Tags
Every HTML page requires 4 tags in this order:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>...</head>
<body>...</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
- Very top of the HTML document
- Tells browser what version of HTML is being used
<html>
- Starts the beginning of the document
- Wrapper of <head> & <body> elements
<head>
- First element inside of a <html> tag
- Content invisible to the reader
- Gives the browser important information about how to interpret the HTML on the page
Other valid tags inside of <head>:
- <title> Text that displays in browser tab
- <meta charset="utf-8"> Character encoding: In HTML5 contains almost all characters & symbols in the world.
Other valid tags inside of <head>:
- <meta> Metadata for search engines and more
- <link> Linked files
Linked File Tag Examples
- <link rel="stylesheet" href="/css/style.css"></link>
- <script src="/javascript-file.js"></script>
Add CSS linked files
Add JavaScript linked files
<body>
- Second element inside of a <html> tag
- Content visible to the reader
Work Time
Worksheet: https://bit.ly/cc-worksheets
Slides: https://bit.ly/cc-html-slides

HTML Content Tags

HTML Content Tags
Live inside the <body> to give your content structure and meaning
HTML Content Tags
- Examples include:
- Headings, Paragraphs,
Lists (Ordered/Unordered) - Hyperlinks, Images, Videos, Audio
- Tables, Figures
- Interactive elements such as:
Buttons, Inputs, Selects
HTML Content Tag Examples
- Navigation, Footer, Address, Quotations, Articles, and Sections
- Divider or Span: containers that group content
- <!-- Comment -->: notes or reminders
Semantic HTML
- Way of organizing content
- Use tags that best convey content meaning
Semantic HTML
For example, you can quote Malala Yousafzai using a <span> or semantically correct <q> tag:
<span>
We realize the importance of our voices only
when we are silenced.
</span>
We realize the importance of our voices only when we are silenced.
<q cite="https://www.goodreads.com/book/malala">
We realize the importance of our voices only
when we are silenced.
</q>
We realize the importance of our voices only when we are silenced.
Semantics Improve:
- (SEO) Search engines and discoverability
- Accessibility and creating inclusive websites
- Keeps code organized
HTML Standards & Best Practices
- Case sensitivity
- Indent nested tags
- Every tag should have a close tag that coordinates with an open tag (with the exception of self-closing tags)

HTML Standards & Best Practices
-
Use line breaks in code for readability
(don't try to mash code together) - Be semantic!
<div>
<h1>Watermelon Moscow Mule</h1>
<h2>
A fruity twist on a classic cocktail
</h2>
<p>
This is one of my favorites! I find it
refreshing on a hot day. The garnish adds a hint of sophistication met with pure
enlightenment.
</p>
<div>
<h2>This drink consists of:</h2>
<ul>
<li>Watermelon</li>
<li>Vodka</li>
<li>Lime juice</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>


Debugging Tools

Debugging Tools
- We are human
- Humans make mistakes
- Tools help troubleshoot unexpected outcomes
Dev Tools in Browser
- Inspect elements on any webpage
- Ways you can inspect elements:
- Right click & inspect
- Windows: CTRL + SHIFT + I
- Mac: CMD + OPT + I
- F12 and open tab for Elements
Validating Your Code
W3C HTML Validator -
https://validator.w3.org/
Scans HTML for mistakes
via direct URL, file upload, or direct input (copy/paste)
Speaking of Validation...
Even those of us in development jobs don't know everything...

...we do know how to utilize resources to find out what we need to know to solve a specific issue

Resources
Peers: ask co-workers or KCWiT on Slack!
Debugging
Classic ways to Debug
- Comment out code
- Uncomment code
- Repeat until you find the issue
Work Time
Worksheet: https://bit.ly/cc-worksheets
Slides: https://bit.ly/cc-html-slides

HTML Tag Attributes

Attributes
- Values added to HTML elements
- Change or adjust the element's behavior
- Set inside the opening tag (including self-closing tags)
attributeName="value here"
Standard attributes
- Supported in all HTML elements
- Only applied to specific elements
- Custom attributes used for unique needs
Important Attributes
idclasshrefsrcdata-*:
id
- Supported in all HTML elements
- Uniquely identifies an element
<p id="#hot-toddy"></p>
class
- Supported in all HTML elements
- Used to group elements
- Use class over id
<p class="hot-toddy"></p>
href
- Specific to hyperlink element
- Provides URL of link
<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Women_in_computing">
Click here to learn about Women in computing</a>
Click here to learn about Women in computing
src
- Specific to image element
<img src="https://arc.net/images/logo.png" alt="Arc logo" />
data
- Custom attributes specific to a website's needs
<div data-menuItem="3">Hot Toddy</div>
Helpful attribute list:
Helpful Tip About Paths
- Used for links and files
- Provides location to image, file, page, or website
- Can be absolute or relative
Relative Paths
- Used for images, files, and links to other pages on the current website domain
- Relative to the current page
index.html
/about/stars.html
Absolute Paths
- Used for images, files, and links to other pages on a different website domain
- Always includes the domain
http://heygirl.io/
heygirl.io
https://awkwardfamilyphotos.com/category/photos/awkward-hall-of-fame/
awkwardfamilyphotos.com
DOM
Document Object Model

Document Object Model
- Web document as data representation
- Browser parses the HTML you write and turns it into the DOM
- Visual representation of the DOM will match the HTML code you wrote
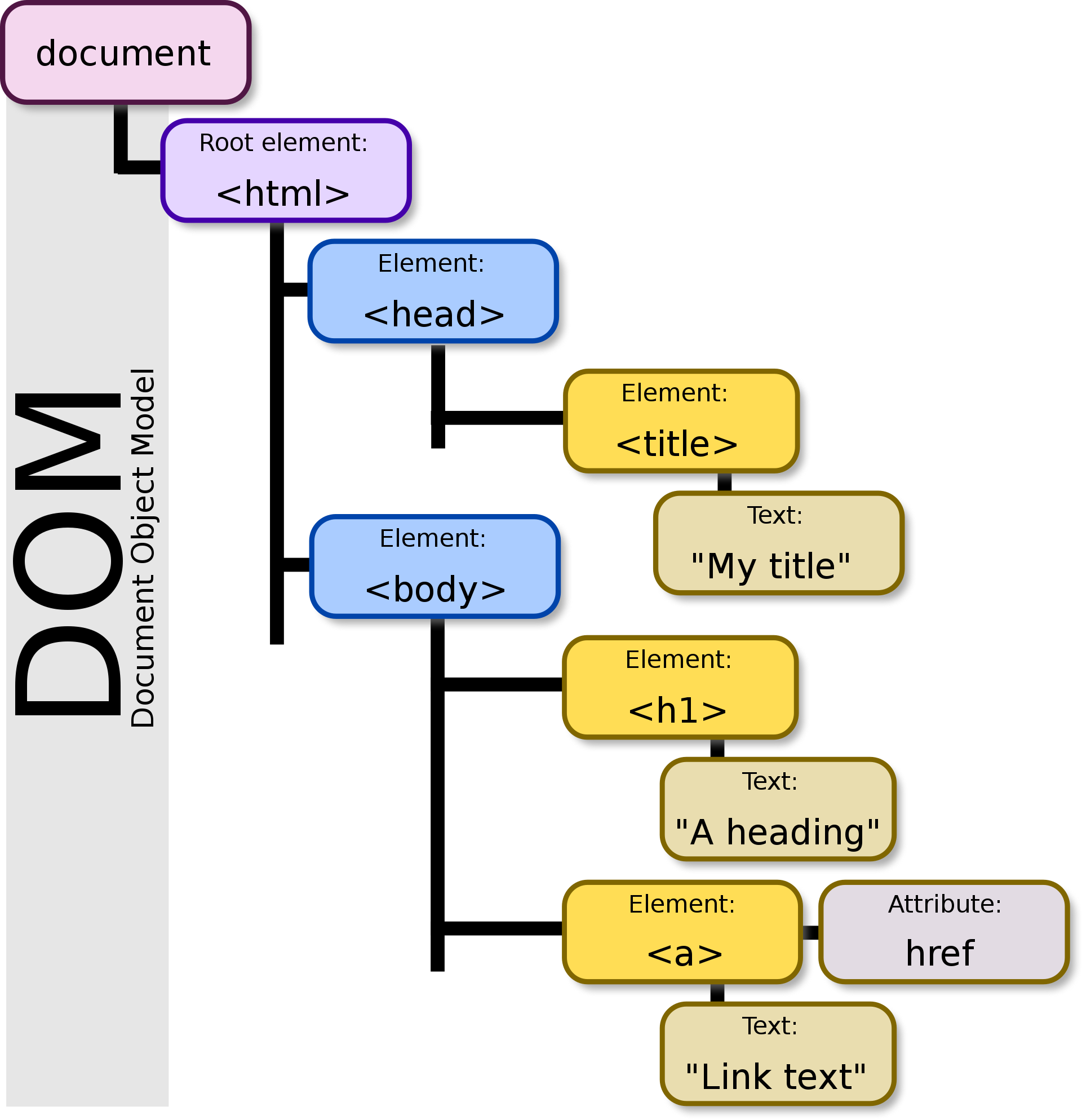
Reasons DOM differs from code:
- Mistakes in your HTML
- Browser will attempt to fix mistakes
- JavaScript
- Can manipulate the DOM (add, change, or remove content, etc.)
Work Time
Worksheet: https://bit.ly/cc-worksheets
Slides: https://bit.ly/cc-html-slides
Accessibility

A11y
- A11y (ahl-lee) is a numeronym (type of abbreviation) for accessibility
- Numeronym: takes the first and last letters of a word & replaces the letters inside with a number representing the letters replaced
Accessibility
- Accessibility
- Numeronym for Accessibility:
- 11 letters between the "a" and "y"
- Another common numeronym is i18n for internationalization
What Is Accessibility?
Making things more usable by members of the disabled community
Why Is It Important?
- A better experience for ALL users
- Expands audience
- Legal obligations (such as ADA) depending on the website
What is POUR?
Framework from WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidlines) to make websites more accessible.
- Perceivable
- Operable
- Understandable
- Robust
WCAG
W3C WCAG 2.0 Guidelines
https://www.w3.org/WAI/standards-guidelines/wcag/
Perceivable
- Provide text alternatives for any non-text content
- Pay attention to things like contrast (especially in text)
- Provide alternative ways to interact with things like video (captions, video descriptions, sign language, etc.)
Operable
- Think how everyone can operate on your site regardless of ability or disability
- Use focus indicators to highlight interactive content
- Avoid things that could trigger seizures or other reactions
Understandable
- Use predictable and consistent navigation & actionable components
- Include useful feedback (form field labels) and error handling messages
- Use clear, simple language and readable fonts
Robust
- Use valid HTML and ARIA attributes
(ARIA labels = content tags for screen readers) - Maximize compatibility with current assistive technology and browsers
- Ensure dynamic content can be accessible without a mouse
Disability Pride Flag
**Disclaimer: Potential trigger for sensitive individuals
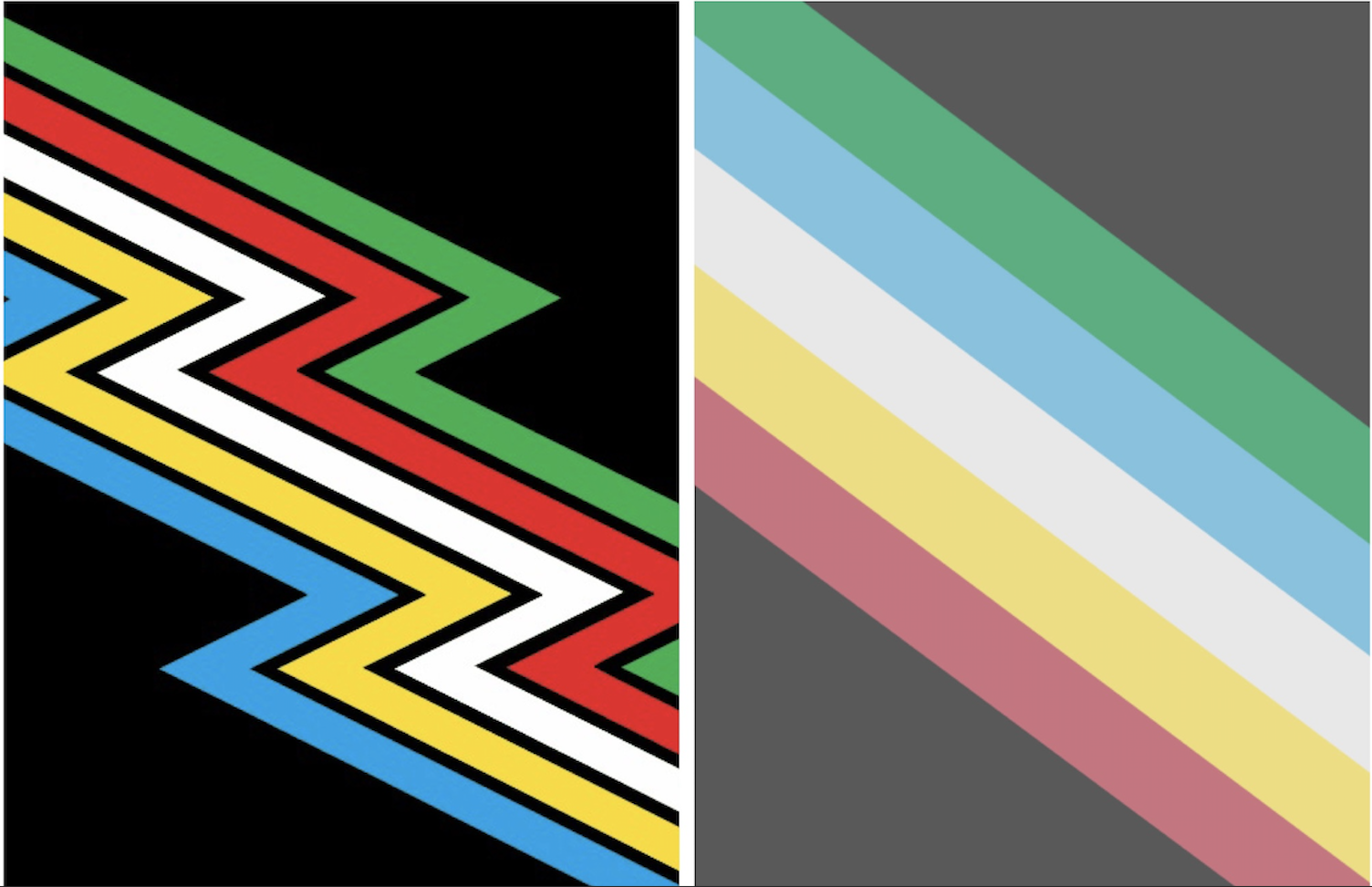

Disability Pride Flag
- Created by: Ann Magill (Cerebral Palsy) in 2019
- Original version caused a strobe/flicker effect when scrolled on electronic devices
- Redesigned in 2021 to be more accessible for people with visual sensitivities
Accessibility Best Practices
- Follow HTML standards and use semantic HTML
- Include information like "alt" text on images
- Use ARIA attributes where needed
- Add keyboard navigation
- Use descriptive URLs for screen readers
Best Practices Continued
- Use sufficient color contrast
- Add label to form fields
- Avoid tiny fonts
- Avoid flashing content
Best Practices Continued
-
Provide visible indication of focus
- :hover with mouse
- :focus without mouse
- Add captions or transcripts for audio/videos
- Listen to user feedback
Accessibility Checkers
- Check your website with an accessibility checker:
Work Time
Worksheet: https://bit.ly/cc-worksheets
Slides: https://bit.ly/cc-html-slides

Intro to Front-End Architecture

Front-End Architecture
- Good architecture is fundamental in building houses
- Same applies to applications/websites
- Different applications/websites can require different structures
Front-End Continued
- We'll cover basics that can be reused for most of your projects
- Of course you can customize as your project requires
What is Front-End Architecture?
Simple definition:
Where files & assets go (how they're organized)
Why Is It Important?
"Easy" to write code
Hard to write maintainable code
This increases as:
- New features are added
- Size of your team scales
Architecture May Vary
- Individual/Team preferences
- Project requirements
- Mobile and/or Desktop
- Frameworks used
What Does This Look Like?
Mostly conceptual
Architecture May Include:
- Naming conventions
- File organization
- Asset organization
Architecture Examples
- Directory namings such as imgs vs. images
- Organizing by section of site or type of asset, such as app/about/css vs. app/css/about
How Did We Apply This Tonight?
Organized image assets

We'll continue to practice Front-End Architecture concepts as we complete the series...
What's Next
- Find a friend
- Take the quiz
- Join Slack
- Finish tonight's worksheet
- Find an online tutorial on Front End Architecture


Register For Next Month's Event


Well Done LadyDevs!!

